Slap Tears
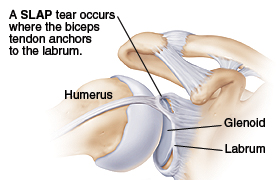
A SLAP tear, also known as a superior labral tear, occurs when part of the shoulder joint known as the labrum is torn. The shoulder is similar to the hip in that they are both ball and socket joints, but the shoulder joint is considerably more shallow and less stable as a result. The labrum helps overcome this instability by forming a “cup” that surrounds the head of the humerus and provides additional support. As a result, when the labrum is torn the shoulder may become considerably less stable.
The most common form of labral tear is the SLAP tear, which stands for Superior Labrum from Anterior to Posterior tear. In a SLAP tear, the top (superior) portion of the labrum is torn completely from front (anterior) to back (posterior), hence the name.
How do SLAP Tears Occur?
SLAP tears are commonly associated with activities like lifting heavy objects, falling onto an outstretched hand, or repetitive overhead actions, such as throwing a football or baseball.
The part of the labrum where a superior labral tear occurs has very few blood vessels, so it is more prone to injury and slower healing. Other parts of the labrum have the ability to heal easier because there is more of a blood supply in the area.
Symptoms of a Superior Labral (SLAP) Tear
Symptoms of a SLAP tear include a painful ‘catching’ sensation when moving the shoulder, usually associated with overhead movements such as throwing. Patients also commonly report pain deep within the shoulder or in the back of the shoulder joint.
Diagnosing a SLAP Tear
Diagnosis of a SLAP tear begins by taking a patient history and performing physical examination tests. Your physician will usually ask specific questions to help indentify symptoms associated with a SLAP tear and how the injury occured.
Because there are a wide variety of shoulder complications, MRI scan may be used to confirm clinical diagnoses. Because the labrum is a small piece of tissue within the shoulder joint, contrast dye must be used to highlight injured areas. This dye will be injected into your shoulder joint during the MRI scan, and allows the physician to find the exact point of injury.
Treatment of a SLAP Tear
Depending on the severity of the tear, your physician may opt for conservative treatment before resorting to surgery. Symptoms of minor tears may be improved with a regimen of phyiscal therapy and anti-inflammatory drugs. Patients must enusre that they continue physical therapy exercises following the end of their regimen to ensure the tear does not get worse.
For larger or more severe tears, your physician may choose to perform a surgical repair of your labrum. This procedure is done arthroscopically, which means that the surgery is entirely done through small poke-hole incisions in the shoulder. A scope and surgical instruments are inserted through said holes and are used to stitch the labrum back into place. This surgery is minimally invasiv and done in an outpatient setting, meaning patients may return home the same day. Following surgery, patients must undergo a regimen of phyiscal therapy to regain strength in their shoulder. A shoulder brace or sling must also be used to keep the labrum in place as it heals.






